How Cow Milking Machines Work: Core Components and Digital Integration
The mechanics of machine milking: mimicking natural calf suckling
Today's cow milking machines work pretty much like how a calf would naturally nurse from its mother. They switch back and forth between soft sucking and letting go, creating this kind of pulse effect that actually helps cows let out their milk more easily and without causing them pain. The design basically copies what happens in nature, which makes sense for the way cows are built. Farmers have noticed that this method works better than just doing it by hand, both in terms of getting more milk out and making sure the cows stay comfortable during the process.
Core components of a cow milking machine: vacuum pump, pulsator, claw, and teat cups
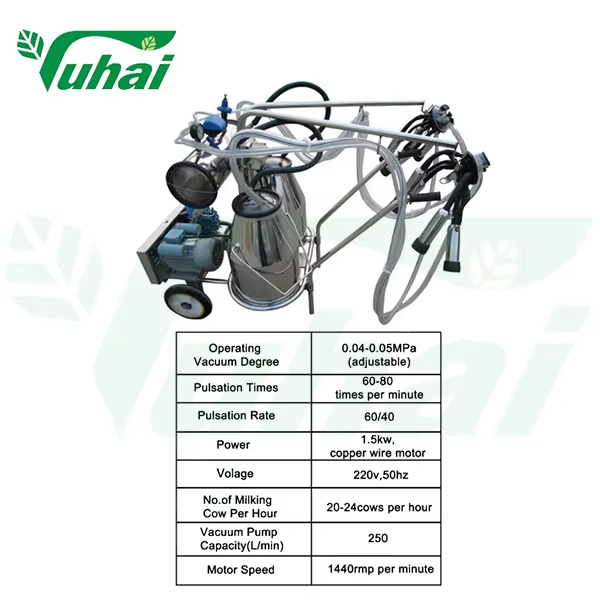
Most modern cow milking machines rely on about four main parts that work together pretty well. There's the vacuum pump which creates suction around 40 to 50 kPa usually. Then we have this pulsator thing that goes through pressure changes roughly 45 to 60 times each minute, kind of like how calves nurse naturally. The teat cups themselves come with those soft inner linings and they stick onto the udder without being too aggressive. Milk gets collected by what's called the claw assembly, which keeps the vacuum steady throughout the process. Farmers notice that when everything works right, cows seem more comfortable during milking sessions, and milk flows out much better than with older methods.
Role of digital sensors in monitoring milk flow and udder health
Modern milking setups are starting to include digital sensors that turn regular milking sessions into something much more than just collecting milk. The sensors track things like how fast milk flows out, check electrical conductivity levels which can indicate if there might be mastitis problems, and even measure milk production from each section of the udder separately. When something looks off, these smart systems will automatically highlight it for farmers to check. Research on dairy tech indicates that farms with these sensor systems catch udder health problems about 30 percent sooner than those without them. This early detection means farmers can act quickly when needed, and often they end up using fewer antibiotics overall since treatments become more specific rather than blanket approaches.
Benefits of Cow Milking Machines: Yield, Quality, and Animal Welfare
Enhanced milk yield and consistency through standardized milking processes
Cow milking machines boost production by ensuring complete and consistent milk extraction. By maintaining optimal vacuum pressure and pulsation rates, these systems maximize average yield per cow. Standardized operation eliminates human variability, leading to uniform milking performance and improved overall productivity across the herd.
Improved milk quality due to reduced contamination risks
Automated systems enhance milk quality by minimizing human contact and environmental exposure. Closed stainless-steel transfer lines prevent airborne contaminants, while rapid cooling preserves freshness. This controlled environment limits bacterial growth, resulting in higher-grade milk with longer shelf life and better compliance with safety standards.
Positive impact on animal welfare with gentle, consistent milking routines
Milking machines support animal welfare through predictable, low-stress routines. Soft teat liners and calibrated vacuum settings mimic natural nursing patterns, reducing physical strain. Automated detachers stop milking once flow drops, preventing over-milking and protecting teat integrity and udder health.
Behavioral benefits for cows: voluntary milking access reduces stress
In robotic setups, voluntary milking allows cows to choose when to be milked based on their natural rhythms. This autonomy reduces anxiety and competition within the herd, minimizing forced handling and movement. As a result, cows exhibit more natural behaviors and experience improved overall well-being.
Industry Paradox: Over-milking risks despite technological precision
Despite automated detachers and advanced sensors, over-milking can still occur if equipment is poorly maintained or improperly calibrated. Prolonged milking sessions may cause teat-end damage and increase mastitis risk. This highlights the importance of regular system checks and oversight–even in highly automated environments–to safeguard animal health.
Automation and Smart Technology in Modern Milking Systems
Evolution from conventional milking to automated milking systems (AMS)
Moving away from hand milking to automated milking systems represents one of the biggest changes in modern dairy farming practices. What started with basic vacuum pumps back in the 70s has now grown into sophisticated robotic setups that actually think for themselves thanks to AI, cameras that can spot when a cow needs attention, and all sorts of sensors tracking everything from udder health to milk quality. Traditional methods required farmers to get up at ungodly hours twice a day just to milk the herd, which was both physically demanding and time consuming. With AMS, cows basically decide when they want to be milked, coming over to the robot whenever it suits them. This change hasn't just made life easier for farmers who no longer have to work those grueling early morning shifts, but also creates much more consistent operations across the entire farm.
Robotics and sensor technology in milking: enabling hands-free operation
Modern robotic milking systems take care of almost everything from start to finish. These machines use laser technology to find where to attach properly, and they have those fancy 3D cameras watching over things too. The cameras check how healthy the udders look and track just how much milk is flowing out during each session. Special robotic arms come with little brushes that clean the teats right before starting and then carefully remove themselves once done. Each cow gets recognized through RFID tags built into the system. This means farmers can see exactly when their animals were milked last, how long it took, and what quantity came out. All this tech works around the clock without needing anyone there, adjusting settings specifically for each individual animal based on its unique needs and habits.
Integration of IoT in dairy farm automation: real-time monitoring and alerts
Connecting milking machines, various sensors around the barn, and farm management programs through IoT technology creates one big working system. The setup keeps gathering information about how much milk cows produce, what's in that milk, and signs about their general well being. All this info gets sent up to online storage spaces where farmers can check it anytime from their phones or desktops. When something goes wrong with milking completion rates, early signs of mastitis showing up, or when machinery starts acting funny, farmers get immediate notifications right away. Real world experience shows farms that have adopted these smart systems tend to react about thirty percent quicker when health problems pop up, and they generally run their operations around twenty five percent better overall compared to traditional methods.
Predictive analytics for health and reproduction using milking data
The data collected from automated milking systems gives farmers valuable insights through predictive analytics that help manage herds more effectively. Smart algorithms look at changes in milk production levels, electrical conductivity readings, and animal behaviors to spot potential health issues, heat cycles, or dietary problems long before they become serious concerns. Some systems can actually predict mastitis cases about two days before any visible symptoms show up, while others pinpoint ideal breeding times with pretty impressive accuracy around 95%. Studies in the dairy sector suggest farms using these technologies tend to cut down on antibiotics by roughly 40%, which is a big deal for both cost savings and animal welfare. Plus, reproductive outcomes improve significantly too, with success rates jumping about 30% over old fashioned observational techniques.
Labor Efficiency and Economic Impact of Cow Milking Machines
Reduction in manual labor by up to 50% with automated milking systems
Milking operations get a lot easier with automated systems taking care of all those repetitive chores that used to eat up so much farmer time. According to field reports from dairy farms across the country, these automated milking setups can slash the need for hands-on work by around half. Think about what that means practically speaking farmers who previously clocked in 6 to 8 hours each day just to milk their cows now find themselves spending only 2 or 3 hours doing similar work for herds of comparable size. The extra time saved isn't just spare change it opens doors for important stuff like keeping closer tabs on animal health, working on long term business strategies, and getting around to fixing that old barn wall everyone keeps putting off.
Shift in farmer role: from physical work to data monitoring and decision-making
Automation changes what farmers actually do day to day. Instead of spending all their time on manual tasks, they now spend more time looking at screens and numbers. Farmers get real time info on how much milk cows are producing, whether any animals seem sick or stressed, and how well the equipment is running. This kind of information helps them make better choices when it comes to feeding schedules, which cows to breed together, and when to call the vet. Many dairy operations report that this shift makes farm work feel more like science than drudgery. Workers often find the job more satisfying since they're not constantly lifting heavy buckets or standing for hours during milking sessions anymore.
Controversy Analysis: High initial cost vs. long-term efficiency gains
Automated milking systems definitely come with a hefty price tag, usually around $150k to $250k for each unit installed on farm. But many dairy operations find they get their money back in about three to five years after installation. What farmers really need to think about is spending this big chunk of cash upfront versus saving money over time by cutting down on labor costs. Labor alone eats up roughly 40 to 50 percent of what it costs to run a regular dairy operation. There are other perks too. Milk production goes up quite a bit when these systems are in place, some farms report increases between 7,000 and even 9,000 liters per cow every year. Plus, cows tend to stay healthier overall, which means fewer vet bills and better returns at the end of the day for most dairy businesses.
Sustainability and Future Trends in Smart Dairy Farming
Reduction in resource use (feed, land, water) through optimized herd management
Smart dairy technologies optimize resource use through precision management. AMS-linked feeding systems deliver customized rations based on individual cow needs, reducing feed waste by up to 15% without compromising production. Pasture utilization improves through data-informed grazing strategies, while efficient cleaning cycles minimize water consumption across operations.
Greenhouse gas emissions reduction via improved feed efficiency and cow health
Enhanced feed efficiency directly lowers methane emissions from enteric fermentation. Healthier cows with balanced diets and reduced stress produce less greenhouse gas per liter of milk. Research shows farms using integrated smart farming solutions can reduce their carbon footprint by up to 20% through better nutrition and proactive health management.
Case example: Dutch farms achieving 30% lower carbon footprint with AMS
The Netherlands has become something of a model for green farming thanks to tech upgrades on dairy farms across the country. According to recent studies on farm sustainability, dairies that use automated milking systems, feed cows with pinpoint accuracy, and manage manure using smart methods tend to produce about 30 percent fewer greenhouse gases compared to traditional farms. What makes these operations stand out is their ability to track data as it happens, allowing farmers to adjust how they run things without compromising on taking good care of the animals or harming the surrounding environment. Many local farmers talk about how these changes not only help the planet but also make sense economically in the long run.
Future projections for dairy technology adoption: global AMS growth expected to double by 2030
The number of farms using automated milking systems around the world could very well double by 2030 according to recent projections. Several factors are pushing this change forward including ever increasing labor expenses, stricter regulations demanding greener practices, plus continuous tech upgrades making these systems better all the time. Experts in the field reckon that somewhere north of 40 percent of big dairy operations across developed countries will have implemented at least basic smart milking solutions within ten years from now. What we're seeing here isn't just about saving money either; dairy farmers are genuinely interested in improving how cows are treated during milking while also reducing their environmental impact. Many see automation as essential for staying competitive in today's market where consumers care increasingly about both animal welfare standards and carbon footprints associated with food production.
FAQs About Cow Milking Machines
1. How do cow milking machines benefit dairy farmers?
Cow milking machines enhance milk yield and quality, reduce manual labor, boost animal welfare, and enable farmers to focus on monitoring herd data for better decision-making.
2. How do digital sensors aid in milking process?
Digital sensors monitor milk flow, udder health, and identify potential problems like mastitis early, allowing for timely interventions and reducing antibiotic usage.
3. What are the economic implications of investing in automated milking systems?
While the initial investment in automated milking systems can be high, they often pay off within three to five years through reduced labor costs and increased milk production.
4. What are the core components of a cow milking machine?
The core components include a vacuum pump, pulsator, claw, and teat cups, all of which work together to mimic natural suckling and ensure effective milk extraction.
Table of Contents
- How Cow Milking Machines Work: Core Components and Digital Integration
-
Benefits of Cow Milking Machines: Yield, Quality, and Animal Welfare
- Enhanced milk yield and consistency through standardized milking processes
- Improved milk quality due to reduced contamination risks
- Positive impact on animal welfare with gentle, consistent milking routines
- Behavioral benefits for cows: voluntary milking access reduces stress
- Industry Paradox: Over-milking risks despite technological precision
- Automation and Smart Technology in Modern Milking Systems
- Labor Efficiency and Economic Impact of Cow Milking Machines
-
Sustainability and Future Trends in Smart Dairy Farming
- Reduction in resource use (feed, land, water) through optimized herd management
- Greenhouse gas emissions reduction via improved feed efficiency and cow health
- Case example: Dutch farms achieving 30% lower carbon footprint with AMS
- Future projections for dairy technology adoption: global AMS growth expected to double by 2030
- FAQs About Cow Milking Machines




